Webhooks
Webhooks let you subscribe to events happening in the OpenAge Engine as they happen, as opposed to polling an API to see if data is available.
Webhooks can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Handling age verification results
Setting up webhooks
Webhooks are configured in the Compliance Studio, by specifying a URL that OpenAge calls when an event occurs. The URL must be a secure HTTPS URL. OpenAge sends a POST request to the URL with a JSON payload that contains the event data.
Webhooks are associated with individual products. You can use the same endpoint for all of your OpenAge Products if you have more than one, but it's important to note that you must retrieve the correct Product-specific OpenAge API Key to make API calls (for example /verification/get-status).
Webhooks can be configured on Developer Settings of a selected product. You can access this page at /products/[productId]/developer.
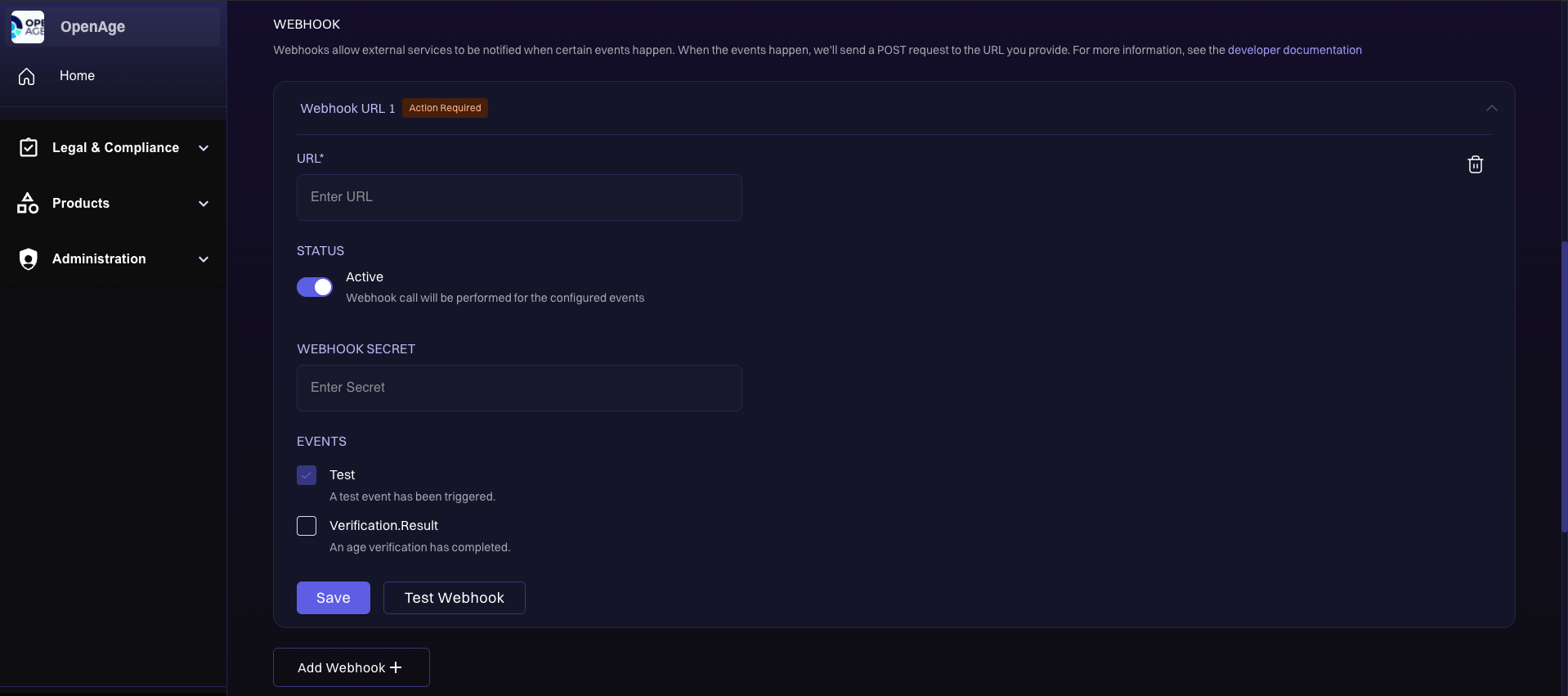
Webhooks configuration page
The Webhooks section in Developer Settings allows you to configure HTTPS URLs for OpenAge to call when specific events occur. By entering the webhook URLs for your app and clicking Save, your configuration is updated in the system. The changes are automatically applied to the appropriate environment - Test Mode or Live Mode, based on your current settings. This ensures that event notifications are routed correctly and securely to your server, whether you're testing or operating in production.
The Save button is different from the Push to Test and Publish Live buttons. While saving and updating a webhook doesn't directly impact your users, changes made using Push to Test or Publish Live can affect the overall user experience and might require a review by the OpenAge team before taking effect.
Additionally, there is a Test Webhook button that allows you to verify if your endpoint is set up correctly, with or without secrets. If a secret is configured, clicking Test Webhook sends two requests to your endpoint: one with a valid signature and one with an invalid signature. The test only passes if your endpoint returns a
200 OK response for the request with the valid signature and a 401 Unauthorized response for the request with the invalid signature. You can find more details on validating webhook requests in the documentation. This button simulates a test event, which you can reference in the test event section of the documentation.
Webhook event structure
The JSON payload sent to the webhook URL contains the following fields:
eventType- The type of event that occurred.data- The data associated with the event.
An X-Event-Type header is also sent with the event type.
Validating webhook requests
Webhooks are sent over the public internet, so it's important to validate that the requests are coming from OpenAge. This is done by verifying the event payload signature with the configured webhook secret.
All requests include the following headers:
X-Signature-Timestamp- The timestamp of the request, in UNIX epoch seconds.X-Signature-Hmac-Sha256- The HMAC SHA-256 keyed-hash of the UTF-8 encoded timestamp and request body concatenated together, using the webhook secret as the key, encoded as a lowercase hexadecimal string.
If the signature is invalid, the request should be rejected with a 401 status code. Webhook requests with validated signatures can be processed and accepted with a 200 status code. When using the Test Webhook button with a configured secret, your endpoint must return 200 for the validly signed request and 401 for the invalidly signed request for the test to pass.
Example code
const crypto = require("crypto");
// Your webhook secret, configured in the Compliance Studio.
const SECRET = "your-secret";
const timestamp = req.get("X-Signature-Timestamp");
const signature = req.get("X-Signature-Hmac-Sha256");
const body = req.rawBody; // Raw request body, as a string.
// Compute the expected signature.
const hmac = crypto.createHmac("sha256", SECRET);
hmac.update(timestamp + body);
const expectedSignature = hmac.digest("hex");
// Compare signatures securely.
if (
!crypto.timingSafeEqual(
Buffer.from(signature, "hex"),
Buffer.from(expectedSignature, "hex")
)
) {
return res.status(401).end("Unauthorized");
}
Webhook event types
The following event types are available:
Test
This event type is used to verify that the webhook is working correctly. It should be handled by the webhook receiver.
Example payload:
{
"eventType": "Test",
"data": {
"id": "12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789abc"
}
}
Verification result
Properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | string | The unique verification ID |
status | string | Can be PASS or FAIL |
ageCategory | string (optional) | The estimated age category. Can be adult, digital-youth, or digital-minor. This is only set if status is PASS |
method | string (optional) | The verification method used. Can be id-document, credit-card, facial-age-estimation, or agekey. This is only set if status is PASS |
failureReason | string (optional) | The reason the verification failed. Can be age-criteria-not-met or max-attempts-exceeded. This is only set if status is FAIL |
age | object (optional) | The age details. This is only set if status is PASS and if the verification scenario is configured to return the age |
age object properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
low | integer | The lower bound of the estimated age. In the case of a hard age verification method, such as an ID document check, this is the exact age |
high | integer | The upper bound of the estimated age. In the case of a hard age verification method, such as an ID document check, this is the exact age |
Example payload:
{
"eventType": "Verification.Result",
"data": {
"id": "5a58e98a-e477-484b-b36a-3857ea9daaba",
"status": "PASS",
"ageCategory": "adult",
"method": "id-document",
"age": {
"low": 25,
"high": 25
}
}
}